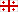
| Blue Screen of Death | The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is an error screen displayed on a Windows computer system after a fatal system error. This critical error causes the system to crash, requiring a restart. Here's a breakdown of what you should know about BSOD What Causes BSOD? - Hardware Issues: Defective hardware components such as RAM, hard drives, or motherboard problems can trigger BSOD.
- Driver Issues: Faulty or incompatible drivers can cause system instability leading to a BSOD.
- Software Conflicts: Conflicts between different software programs or malware infections can result in system crashes.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause hardware components to malfunction, leading to a BSOD.
- Corrupted System Files: Critical system files that are corrupted or missing can cause the operating system to fail.
How to Diagnose BSOD? - Error Code: When a BSOD occurs, an error code is displayed. This code can help identify the cause of the crash.
- Minidump Files: Windows creates a minidump file when a BSOD occurs. These files contain information that can be analyzed to determine the cause of the crash.
- Event Viewer: Windows Event Viewer logs detailed information about system events, which can help diagnose the root cause.
Common BSOD Error Codes - 0x0000007B (INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE): Indicates a problem with the system's boot device, such as a failed hard drive.
- 0x00000050 (PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA): This error occurs when the system tries to access invalid memory.
- 0x0000001E (KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED): Caused by driver issues or incompatible hardware.
- 0x0000003B (SYSTEM_SERVICE_EXCEPTION): Indicates a problem with system services, often related to software or driver issues.
Preventing BSOD - Keep Drivers Updated: Ensure all hardware drivers are up-to-date.
- Regular System Maintenance: Run regular system checks and maintenance tasks to keep the system healthy.
- Stable Software Installation: Install only reliable and stable software, and avoid software conflicts.
- Monitor Hardware Health: Regularly check hardware components for signs of failure or overheating.
What to Do When You Encounter a BSOD? - Restart the Computer: Often, a simple restart can resolve temporary issues.
- Check for Updates: Ensure that Windows and all drivers are updated.
- Run Diagnostics: Use built-in tools like Windows Memory Diagnostic and Check Disk to identify hardware issues.
- Consult Minidump Files: Analyze the minidump files to understand the specific cause of the crash.
|